In an interconnected global economy, logistics and supply chain management are two vital components that drive businesses toward success. These terms are often used interchangeably, but they encompass different aspects of moving goods and services from production to the consumer. Understanding the nuances between logistics and supply chain management is crucial for companies aiming to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and deliver superior value to customers.
In this blog, we will have a look at the definitions and differences between logistics and supply chain management, explore their interdependence, and highlight why both are fundamental for business success.
Join our LinkedIn Network for updates, tips, professional growth and many more:
What is SAP Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
Logistics management refers to the process of planning, implementing, and controlling the efficient, cost-effective flow of goods, services, and information from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It encompasses a variety of activities, including transportation, warehousing, inventory management, order fulfillment, and packaging. The primary goal of logistics is to ensure that the right product reaches the right customer at the right time, in the right condition, and at the right cost.
What is Logistics in the Supply Chain?
SAP Supply chain management (SCM) is a broader concept that encompasses the entire network of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. SCM integrates supply and demand management within and across companies, ensuring that all components of the supply chain work together seamlessly to meet customer needs. This includes sourcing raw materials, production, distribution, and delivering the final product to the consumer. The ultimate goal of supply chain management is to create a competitive advantage by enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the supply chain.
While logistics focuses specifically on the movement and storage of goods within the supply chain, supply chain management takes a more holistic approach, integrating all aspects of the supply chain, from raw material acquisition to final delivery.
Supply Chain Management vs. Logistics
Logistics management and supply chain are integral to the efficient operation of any business. However, they serve different purposes within the broader business strategy. While logistics is a component of supply chain management, SCM encompasses a wider range of activities, including logistics, procurement, production, and distribution.
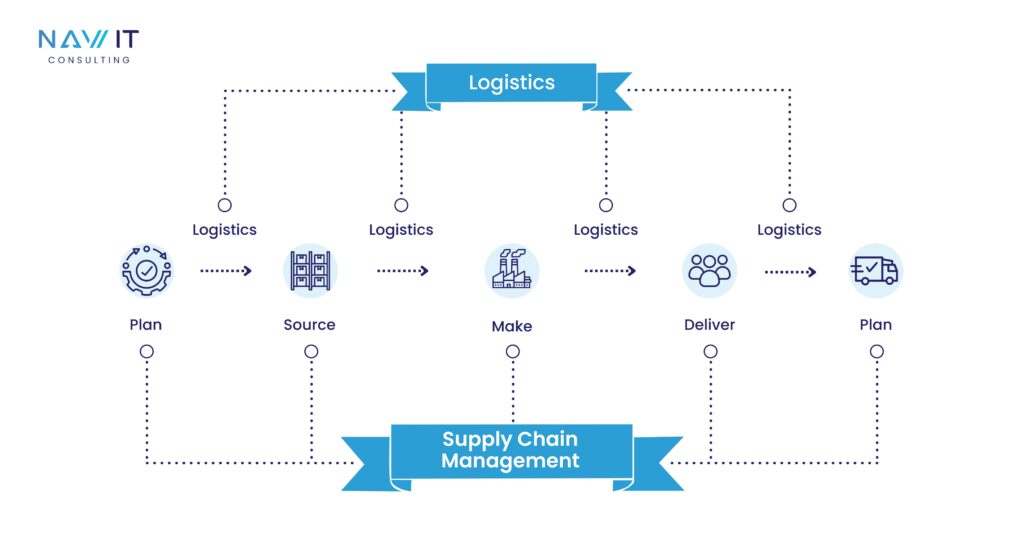
- Scope
Logistics deals with the movement, storage, and flow of goods, services, and information. Supply chain management, on the other hand, covers the end-to-end coordination and management of all activities involved in delivering a product or service to the customer.
- Focus
The primary focus of logistics is on operational efficiency and cost reduction within the supply chain. SCM, however, is concerned with the overall integration and optimization of the supply chain to create a competitive advantage.
- Activities
Logistics involves specific activities such as transportation, warehousing, and inventory management. SCM encompasses these activities and also includes procurement, production planning, supplier relationship management, and demand forecasting.
How Do Logistics and Supply Chain Management Work Together?
Despite their differences, supply chain management and logistics share several common goals and functions. Both are essential to the smooth operation of a business and contribute to customer satisfaction.
1. Shared Goals
- Customer Satisfaction: Both logistics and supply chain management aim to meet or exceed customer expectations by ensuring that products are delivered on time, in the right quantity, and in good condition.
- Cost Efficiency: Both disciplines seek to minimize costs while maintaining or improving the quality of service. This involves optimizing transportation routes, reducing inventory holding costs, and improving operational efficiency.
- Flexibility and Responsiveness: Logistics and supply chain management both strive to create a flexible and responsive supply chain that can adapt to changes in demand, market conditions, and other external factors.
2. Common Functions
- Transportation Management: Both logistics and SCM involve managing the movement of goods from one location to another, whether by road, rail, air, or sea. This includes selecting the most efficient and cost-effective transportation methods.
- Inventory Management: Both disciplines involve managing inventory levels to ensure that products are available when needed while minimizing the cost of holding excess stock.
- Order Fulfillment: Logistics and SCM both include processes for picking, packing, and shipping products to customers, ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time.
How Are Logistics and Supply Chain Management Different?
While Logistics and Supply Chain Management share some similarities, they differ in scope, focus, and objectives.
Scope
- Logistics: The scope of logistics is more narrow and focused on the movement and storage of goods. It deals with the operational aspects of getting products from point A to point B.
- Supply Chain Management: SCM has a broader scope that includes not only logistics but also procurement, production, distribution, and customer service. SCM is concerned with the entire supply chain, from raw material acquisition to final delivery.
Focus
- Logistics: The focus of logistics is on optimizing specific functions within the supply chain, such as transportation and warehousing, to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
- Supply Chain Management: SCM focuses on the overall integration and coordination of all supply chain activities to create a seamless and efficient process. This includes managing relationships with suppliers, coordinating production schedules, and ensuring that all parts of the supply chain work together to meet customer demand.
Objectives
- Logistics: The primary objective of logistics is to deliver products to customers in the most efficient and cost-effective manner possible.
- Supply Chain Management: SCM aims to create a competitive advantage by optimizing the entire supply chain, improving overall efficiency, reducing lead times, and enhancing customer satisfaction.
The Differences Between Supply Chain Management and Logistics
To further clarify the differences between logistics management and supply chain, let’s examine specific examples and how these distinctions impact business operations.
Example 1: Transportation
- Logistics: In logistics, transportation focuses on the efficient movement of goods from one location to another. This includes selecting the best mode of transportation, optimizing routes, and managing the associated costs.
- Supply Chain Management: In SCM, transportation is just one component of the overall supply chain. SCM considers how transportation decisions impact other parts of the supply chain, such as inventory levels and production schedules. For example, choosing a faster but more expensive transportation method may reduce lead times and improve customer satisfaction, but it could also increase overall supply chain costs.
Example 2: Inventory Management
- Logistics: In logistics, inventory management focuses on maintaining optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing the costs of holding excess stock. This includes managing warehousing, order fulfillment, and inventory tracking.
- Supply Chain Management: In SCM, inventory management is part of a larger strategy to optimize the entire supply chain. SCM considers how inventory levels impact production schedules, supplier relationships, and customer satisfaction. For example, reducing inventory levels may lower holding costs, but it could also increase the risk of stockouts and disrupt the supply chain.
Example 3: Supplier Relationships
- Logistics: In logistics, supplier relationships are primarily focused on ensuring the timely delivery of goods and materials needed for production or order fulfillment.
- Supply Chain Management: In SCM, managing supplier relationships is a key component of the overall strategy. SCM involves selecting suppliers, negotiating contracts, managing supplier performance, and ensuring that suppliers meet the company’s quality and delivery standards. Effective supplier management is crucial for creating a resilient and responsive supply chain.
Join our LinkedIn Network for updates, tips, professional growth and many more:
Role of Logistics in Supply Chain Management
Logistics plays a crucial role in the broader supply chain management framework. It is the backbone of the supply chain, ensuring that products move efficiently from one stage to the next.
Key Functions of Logistics in SCM
- Transportation: Logistics is responsible for managing the movement of goods between suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and customers. This includes selecting the best transportation methods, optimizing routes, and managing transportation costs.
- Warehousing: Logistics involves managing the storage of goods at various points in the supply chain. This includes optimizing warehouse locations, managing inventory levels, and ensuring that products are stored in a way that minimizes damage and deterioration.
- Inventory Management: Logistics is responsible for managing inventory levels to ensure that products are available when needed while minimizing the cost of holding excess stock. This includes forecasting demand, managing stock levels, and implementing inventory control systems.
- Order Fulfillment: Logistics involves managing the process of picking, packing, and shipping products to customers. This includes ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time, and managing returns and exchanges.
- Coordination with Other Functions: Logistics must coordinate with other functions within the supply chain, such as procurement, production, and distribution, to ensure that all parts of the supply chain work together seamlessly.
- Optimization of the Supply Chain: Logistics plays a key role in optimizing the overall supply chain by improving transportation efficiency, reducing inventory costs, and ensuring that products are delivered to customers in a timely manner.
Why Use Logistics Management and Supply Chain?
Effective logistics management and supply chain are essential for businesses to operate efficiently and meet customer expectations. Implementing these practices offers several benefits that contribute to operational efficiency and overall business success.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing transportation routes, reducing inventory holding costs, and improving operational efficiency, businesses can significantly reduce their overall costs.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: Effective logistics and supply chain management ensure that products are delivered to customers on time, in the right quantity, and in good condition, leading to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased Flexibility: A well-managed supply chain can quickly adapt to changes in demand, market conditions, and other external factors, allowing businesses to respond more effectively to challenges and opportunities.
- Enhanced Competitive Advantage: By integrating and optimizing all aspects of the supply chain, businesses can create a competitive advantage, improving their ability to meet customer needs and differentiate themselves from competitors.
The Fundamental Role of Supply Chain Management and Logistics in Business Success
Both supply chain management and logistics are fundamental to business success, as they ensure that products move efficiently from suppliers to customers, meet customer expectations, and create a competitive advantage.
Examples of Successful Companies
- NAV IT: NAV IT stands out in the supply chain management and logistics sector by providing advanced solutions that help businesses optimize their operations. Through its innovative technology and strategic insights, NAV enhances visibility, improves decision-making, and streamlines processes for companies across various industries. This approach not only drives efficiency but also supports scalable growth, reinforcing NAV’s role as a key player in modern supply chain and logistics management.
- Amazon: Amazon’s success can be attributed to its highly efficient supply chain and logistics operations, which allow the company to deliver products to customers quickly and cost-effectively. By leveraging advanced technology, optimizing transportation routes, and managing inventory levels effectively, Amazon has created a competitive advantage that has helped it become one of the world’s largest e-commerce companies.
- Walmart: Walmart’s success is also due in part to its effective supply chain and logistics management. By optimizing its supply chain, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency, Walmart has been able to offer low prices and meet customer demand consistently, making it one of the world’s largest and most successful retailers.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences and similarities between logistics and supply chain management is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize their operations and create a competitive advantage. While logistics focuses on the movement and storage of goods within the supply chain, supply chain management takes a broader approach, integrating all aspects of the supply chain to create a smooth and efficient process. Both disciplines are fundamental to business success, as they ensure that products move efficiently from suppliers to customers, meet customer expectations, and create a competitive advantage. By implementing effective logistics and supply chain management practices, businesses can reduce costs, improve operational efficiency, and achieve higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.