AI and Automation are often used like close synonyms, which is far from true. Mistaking one for the other is one of the biggest reasons businesses invest in technology and walk away defeated.
Automation is about consistency. Artificial Intelligence is about intelligence. One executes what you already know. The other helps you deal with what you don’t.
Many organisations struggle with tangled workflows, frustrated teams, and disappointing returns on technology. The reason? They never fully understood the Difference Between AI and Automation from the beginning.
When done right, operations feel lighter, move faster, and adapt more easily. Done wrong, and you’re left with expensive systems that people don’t trust—and won’t use as intended This blog breaks down AI vs Automation clearly—what they are, how they differ, where they overlap, and how to actually use them in real business environments without the hype.
What is Automation?
Automation is the execution of predefined rules at scale. Nothing more, nothing less.
Imagine sorting hundreds of customer emails every day. Each email that contains the word “refund” goes to billing. Anything with “delivery” goes to logistics. No thinking involved. Just rules being followed exactly as written.
That’s automation at work.
At its core, Automation and AI differ because automation depends entirely on human intelligence upfront. People decide the logic. Machines simply carry it out—quickly, repeatedly, and without deviation.
In mid-sized logistics companies without automation, staff spend hours matching invoices to purchase orders. It is rather dull, error-prone, and expensive. By automating the matching logic, you get both results and relief.
Teams can finally focus on supplier negotiations and cost control instead of staring at spreadsheets.
Automation shines when:
The task is repetitive
Errors are costly
Volume is high
Common examples include data entry, invoice processing, payroll, inventory updates, system alerts, and basic quality checks.
Automation doesn’t improve itself. It doesn’t adapt. If conditions change, humans must step in and rewrite the rules. But when the environment is predictable, automation works smoothly. Some may even claim that it can have the upper hand on AI Automation solutions.
What does Artificial Intelligence mean?
The catalyst of movement for Artificial Intelligence is data, and not predefined rules.
Instead of being told what to do at every step, the system is exposed to large volumes of information and allowed to learn patterns over time. In practice, Artificial Intelligence and Automation work very differently here, even when they sit inside the same workflow.
When an AI model is trained on thousands of customer conversations, it starts recognising sentiment without those signals being manually defined. Give it historical sales data, and it learns demand patterns. Show it images of defective and non-defective products, and it learns what “good” and “bad” look like.
This isn’t science fiction. It’s narrow AI—the practical kind already embedded in voice assistants, recommendation engines, fraud detection systems, and chatbots.
We’ve seen this shift firsthand. A retail chatbot initially relies on scripted responses. It works, but not well enough. Once AI Automation is layered in, the bot begins understanding intent instead of keywords. It handles unpredictable queries with empathy and accuracy. Escalations drop. Customer satisfaction rises.
Artificial intelligence flourishes amidst the mess of the real world. This is exactly what AI Automation is in practice.
AI vs Automation: How are they different?
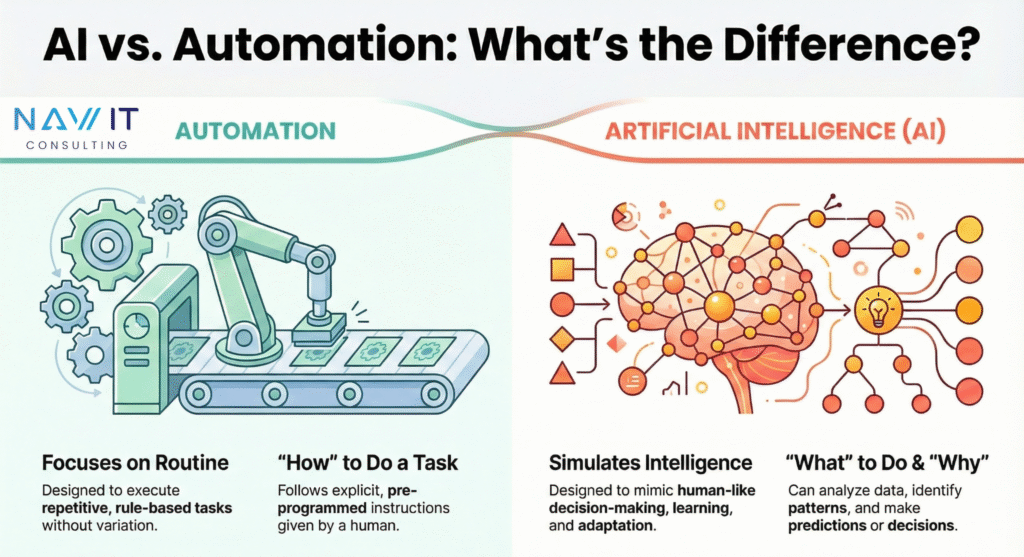
Automation follows instructions.
AI makes decisions.
Understanding AI vs Automation means recognising that automation requires humans to anticipate every scenario in advance. AI handles situations humans didn’t plan for.
Hand a traditional automation system a misspelled keyword or an unexpected input, and it breaks. Hand the same problem to AI, and it infers meaning, learns from context, and moves forward.
The difference between Automation and AI isn’t competition. It’s capability.
Automation is reliable but rigid.
AI is flexible but probabilistic.
Used together, they become powerful. Used incorrectly, they frustrate everyone involved.
Similarities between AI and Automation
Despite their differences, AI and Automation know one target: efficiency.
Both aim to:
Reduce manual effort
Increase speed
Minimise errors
Scale operations without scaling headcount
Whether it’s a factory line assembling parts or an office processing reports, both technologies free humans from repetitive work and redirect energy toward strategy, creativity, and judgment.
Many people ask, “Is Artificial Intelligence and Automation the same?” The answer is no—but they’re partners. They solve different parts of the same problem.
Automation handles execution.
AI handles uncertainty.
Intelligent Automation – The Intersection of AI and Automation
Intelligent Automation is the interesting crossover episode that businesses look forward to. It’s where AI and Automation intersect.
This is the point where AI makes decisions and automation carries them out. Rules are no longer static. They’re informed by learning systems that understand context. This is the practical answer to What is AI Automation?
For example:
Emails aren’t just sorted—they’re analysed for urgency and sentiment using Artificial Intelligence in Automation
Support tickets aren’t just routed—they’re prioritised and partially resolved through AI in Automation
Inventory systems don’t just reorder—they anticipate shortages using AI Automation Solutions
A manufacturing client once combined AI forecasting with automated procurement. AI predicted material shortages weeks in advance. Automation placed orders and updated schedules automatically. The result was fewer stoppages and better cash flow—one of the clearest Benefits of AI in Automation I’ve seen in practice.
Types of AI Used in Automation
Different AI capabilities serve different automation needs within Artificial Intelligence and Automation systems.
Machine Learning
Learns from historical data to predict outcomes like demand, churn, or failure rates. It’s the muscle of AI Automation.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Understands and interprets human language—emails, chats, reviews, and documents—powering AI in Automation
Computer Vision
Analyses images and video to detect defects, verify compliance, or monitor activity in Automation and AI pipelines
Optical Character Recognition (OCR)
Extracts text from scanned documents, invoices, and handwritten forms—bridging What is Automation? with intelligence
Speech Recognition
Converts spoken language into structured data for analysis and action using Artificial Intelligence in Automation
Expert Systems
Encodes specialised knowledge to support diagnostics and decision-making across AI Automation Solutions
Each of these slots into automation pipelines differently. The key is not to use all of them—but to use the right one where rules alone fall short in Automation vs AI decisions.
The Benefits of AI in Automation
The most obvious Benefits of AI in Automation are efficiency and scale. But the real value runs deeper.
AI reduces the need for constant human intervention. It handles edge cases that would otherwise clog workflows. It improves accuracy over time instead of degrading—something traditional What is Automation? systems cannot do.
Teams I’ve worked with report:
Faster response times
Fewer escalations
Higher customer satisfaction
Better decision confidence
AI-driven automation also enables 24/7 operations that don’t just run but think. They spot issues early. They adapt to change. They generate insights humans can act on.
Automation vs AI isn’t a debate about replacement. It’s about capability expansion through AI and Automation working together.
AI and Automation Use Cases
Across industries, AI and Automation Use Cases continue to grow through real operational deployments.
Customer Service
AI classifies and prioritises queries. Automation resolves common issues and routes complex ones—classic AI Automation.
Manufacturing
Vision AI detects defects mid-production. Automation removes faulty units instantly using Artificial Intelligence in Automation
Finance
AI identifies fraud patterns. Automation blocks transactions and triggers investigations—high-trust Automation AI Solutions
Healthcare
AI assists with triage. Automation schedules care and manages records through AI in Automation
Retail
AI personalises recommendations. Automation updates inventory and pricing via AI Automation Solutions
Software Testing
AI identifies vulnerable areas. Automation generates and updates test cases dynamically—advanced Automation and AI
These aren’t experimental deployments. They’re operational advantages being realised today through Intelligent Automation.
Agentic AI: The Latest Evolution of Automation
Agentic AI is the latest innovation staring us in the face.
Instead of responding to instructions, agentic systems pursue goals. They plan steps, use tools, monitor progress, and adjust strategies independently—an evolution beyond traditional What is Automation?
In QA environments, AI agents now:
Explore applications
Identify defects
Write test cases
Adapt as code changes
The key difference is autonomy—but with guardrails. Humans define objectives and boundaries. Agents handle execution and iteration. This reduces micromanagement while increasing throughput on complex tasks using AI Automation Solutions.
Agentic AI doesn’t replace oversight. It replaces coordination overhead in AI vs Automation environments.
Implement an AI Automation Solution in Your Organization
Successful implementation starts with clarity—not technology.
Identify friction points first. Where are teams slowed down? Where do errors repeat? Where does volume overwhelm judgment? These questions determine whether Automation vs AI or Intelligent Automation is required.
Then match the problem to the solution:
Rules-heavy → What is Automation?
Pattern-heavy → Artificial Intelligence in Automation
Both → AI Automation
Start small. Pilot on one workflow. Measure outcomes rigorously—speed, accuracy, satisfaction. Train teams early. Expand only when value is proven.
The best implementations don’t chase transformation. They earn trust incrementally through Automation and AI maturity.
AI and Automation can be seen everywhere, from smart assistants to predictive apps. Businesses that embrace them thoughtfully gain momentum that others struggle to match.
Common Mistakes Businesses Make with AI and Automation
One of the most common mistakes businesses make is starting with tools instead of problems. Teams buy platforms promising AI Automation Solutions without a clear use case. The result is impressive dashboards with very little operational impact.
Another common mistake is trying to automate a broken process. If workflows are unclear, inconsistent, or dependent on tribal knowledge, automation will only double down the dysfunction. AI may even learn the wrong patterns—undermining Benefits of AI in Automation entirely.
Many organisations also underestimate change management. Employees often resist AI and Automation not out of fear of technology, but fear of loss of control. The most successful rollouts position AI as an assistant, not a replacement.
Data quality is another silent failure point. Businesses expect Artificial Intelligence in Automation to compensate for poor inputs. It won’t. Clean data enables reliable Automation AI Solutions.
Finally, there’s the assumption that AI should work perfectly from day one. Unlike What is Automation?, AI improves with feedback. Without review loops, organisations abandon AI too early—misreading learning as failure.
Use Cases for Intelligent Automation Tools
Intelligent Automation usually enters the conversation when existing systems start showing strain. Rules-based workflows reach their limits, volumes increase, and decisions begin to outpace human response time. This is the point where AI and Automation stop being separate ideas and start working together out of necessity.
For many teams, the Difference Between AI and Automation becomes clear only after repeated friction. What once worked through simple automation no longer adapts. That is when questions around What is Automation? shift toward What is AI Automation? — not as theory, but as a practical next step.
Below are common AI and Automation Use Cases where Intelligent Automation is applied because scale, variability, and speed collide.
Customer Support and Experience
Customer support is often where the AI vs Automation discussion becomes unavoidable. Rule-based automation can move tickets from one queue to another, but it often falls short when intent isn’t obvious or when tone and emotion change the meaning of a request.
With AI in Automation, incoming queries are read more carefully — intent, urgency, and sentiment are evaluated first, and only then are the next actions triggered. Automation and AI then resolve repetitive issues automatically, while complex cases are routed to the appropriate teams.
This approach reduces inconsistent responses and unnecessary escalations. These AI Automation Solutions are increasingly used by support teams that need to maintain service quality without continuously expanding headcount, highlighting tangible Benefits of AI in Automation in customer-facing operations.
Finance and Accounting Operations
Finance teams typically approach Artificial Intelligence in Automation with caution. Accuracy, compliance, and auditability don’t allow much room for trial and error. That’s why in finance, Automation vs AI usually isn’t an either–or decision.
Automation is used where consistency matters most — reconciliations, approvals, routine compliance checks. AI Automation comes in later, once volumes grow and patterns start changing, to flag anomalies, anticipate payment delays, and surface risk signals that fixed rules stop catching.
Over time, teams begin to rely on these setups as Automation AI Solutions, not because control is removed, but because problems show up earlier and fewer people are needed to manually sift through high-volume transactions.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
Supply chains expose the limits of static automation quickly. Demand patterns don’t stay still. Supplier performance varies. And manual monitoring rarely keeps up for long.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation have enabled demand forecasting models to collect early signals of shortages or excess stock, before those shifts metamorphose into operational issues. Automation and AI then trigger procurement actions, adjust inventory levels, and update schedules without waiting for manual inputs.
For many organisations, this is the first point where What is AI Automation? becomes clear in operational terms — fewer disruptions, improved working capital, and tighter coordination across suppliers and internal teams.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
In manufacturing environments, AI and Automation Use Cases are driven by real-time requirements rather than experimentation.
Computer vision systems built on Artificial Intelligence in Automation inspect products as they move through production lines. When defects are detected, automation removes affected units immediately and records the incident for further analysis.
This combination of AI Automation and execution reduces waste, maintains throughput, and enforces quality standards without slowing operations.
Human Resources and Talent Management
HR functions manage large volumes of data while still relying heavily on manual coordination. This makes them well suited for AI in Automation when implemented carefully.
AI screens resumes, identifies skill matches, and highlights attrition risks based on historical data. Automation and AI handle interview scheduling, onboarding workflows, and system updates that typically consume disproportionate administrative time.
These AI Automation Solutions allow HR teams to focus more on decision-making and employee engagement, reinforcing practical Benefits of AI in Automation beyond cost savings.
IT Operations and Software Testing
IT environments change frequently, which limits the effectiveness of rigid automation alone. This is where Automation and AI operate most closely together.
Intelligent automation tools monitor systems, predict failures, and trigger remediation workflows. In testing environments, Artificial Intelligence and Automation identify high-risk code areas, while automation generates and maintains test cases as systems evolve.
These Automation AI Solutions help reduce downtime and improve release stability in environments where conditions change faster than manual processes can respond.
Healthcare Administration
Healthcare organisations apply AI and Automation primarily to operational processes rather than clinical judgement.
AI supports triage prioritisation, risk scoring, and diagnostic assistance, while automation manages scheduling, billing, and records. Within this context, Artificial Intelligence in Automation reduces administrative burden without displacing professional oversight.
This application of AI in Automation allows medical teams to spend less time on documentation and more time on patient-facing responsibilities.
Conclusion:
The conversation around AI vs Automation often misses the point. The real value doesn’t lie in choosing one over the other—it lies in combining them intelligently.
Automation excels where certainty matters. AI thrives where variability is unavoidable. Intelligent Automation brings both together, allowing organisations to scale operations without becoming rigid or fragile.
The Difference Between AI and Automation is not about replacement. It’s about capability. Automation executes. AI learns. Together, they form systems that are faster, smarter, and more resilient.
Businesses that succeed with AI and Automation don’t chase trends or tools. They start with problems, build trust incrementally, and expand only when value is proven. They understand that AI Automation Solutions are operating model decisions, not IT experiments.
As environments grow more complex and expectations rise, organisations that embed Artificial Intelligence and Automation into their core workflows will move from reacting to predicting, from executing to optimising.
That’s the real promise of intelligent automation—not hype, not shortcuts, but sustainable advantage built on clarity, discipline, and design.
FAQs on AI and Automation
1. How are AI and automation similar?
2. Is AI and automation the same?
3. What is AI and automation?
4. How can I use AI and automation in everyday life?
5. What is AI and ML in test automation?
6. What is the difference between AI and automation?
FAQs on AI and Automation
1. How are AI and automation similar?
Both reduce repetitive work, improve speed, and increase accuracy—core goals of AI and Automation.
2. Is AI and automation the same?
No. Automation follows rules. AI learns and adapts. Together, they form Intelligent Automation.
3. What is AI and automation?
A combination of execution and intelligence that enables scalable, adaptive operations through AI Automation.
4. How can I use AI and automation in everyday life?
Smart scheduling, predictive reminders, automated shopping, and assistants—common AI and Automation Use Cases.
5. What is AI and ML in test automation?
Machine learning helps testing systems adapt, identify risks, and update tests—advanced Artificial Intelligence in Automation.
6. What is the difference between AI and automation?
Automation executes predefined tasks. AI makes decisions and improves over time—the core Difference Between AI and Automation.
One practical way to think about AI vs Automation is through risk tolerance. Automation is safest when certainty matters most. AI accepts uncertainty to gain adaptability—this distinction shapes modern AI Automation Solutions.
The real Difference Between AI and Automation isn’t technological. It’s philosophical. Automation assumes predictability. AI assumes change. The smartest systems design for both—and that is the true power of Intelligent Automation.